-
Europe’s stagnating heating transition threatens to lock in fossil fuel dependency while undermining the competitiveness of its cleantech manufacturing sector.
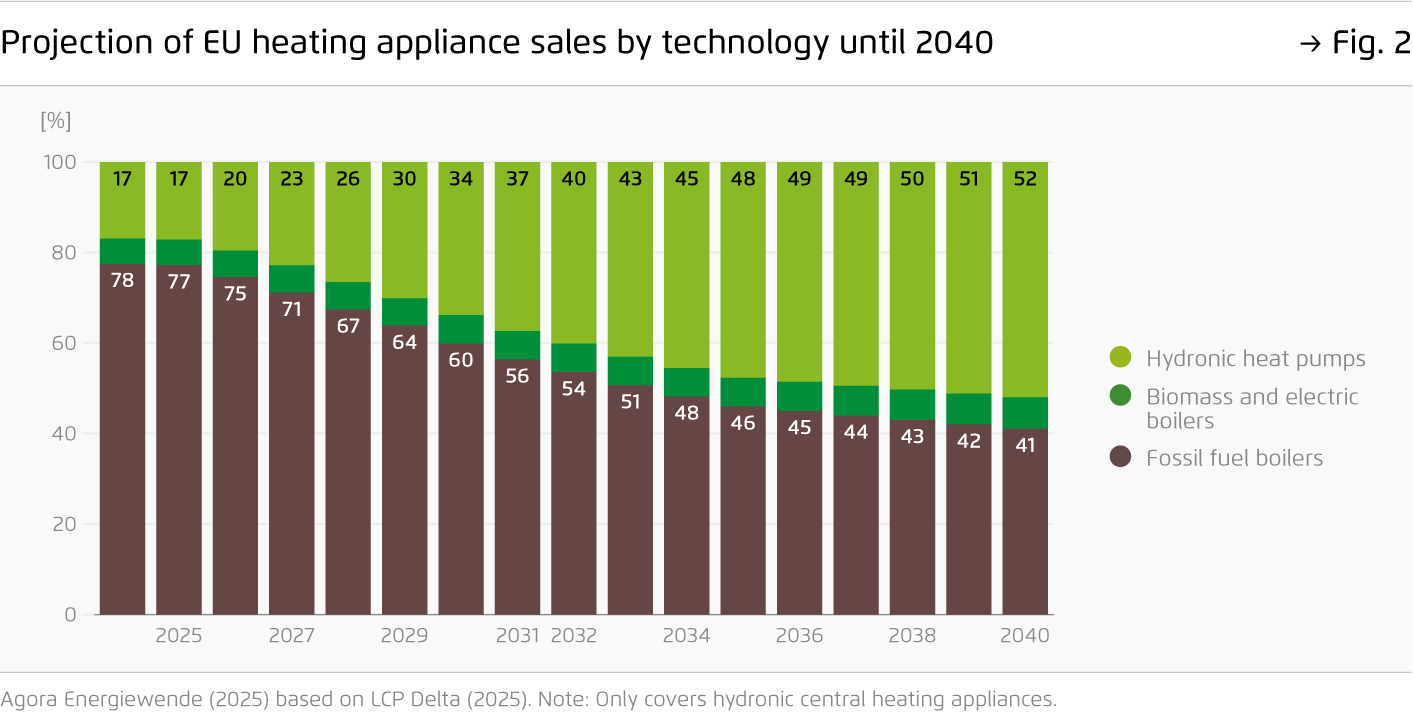
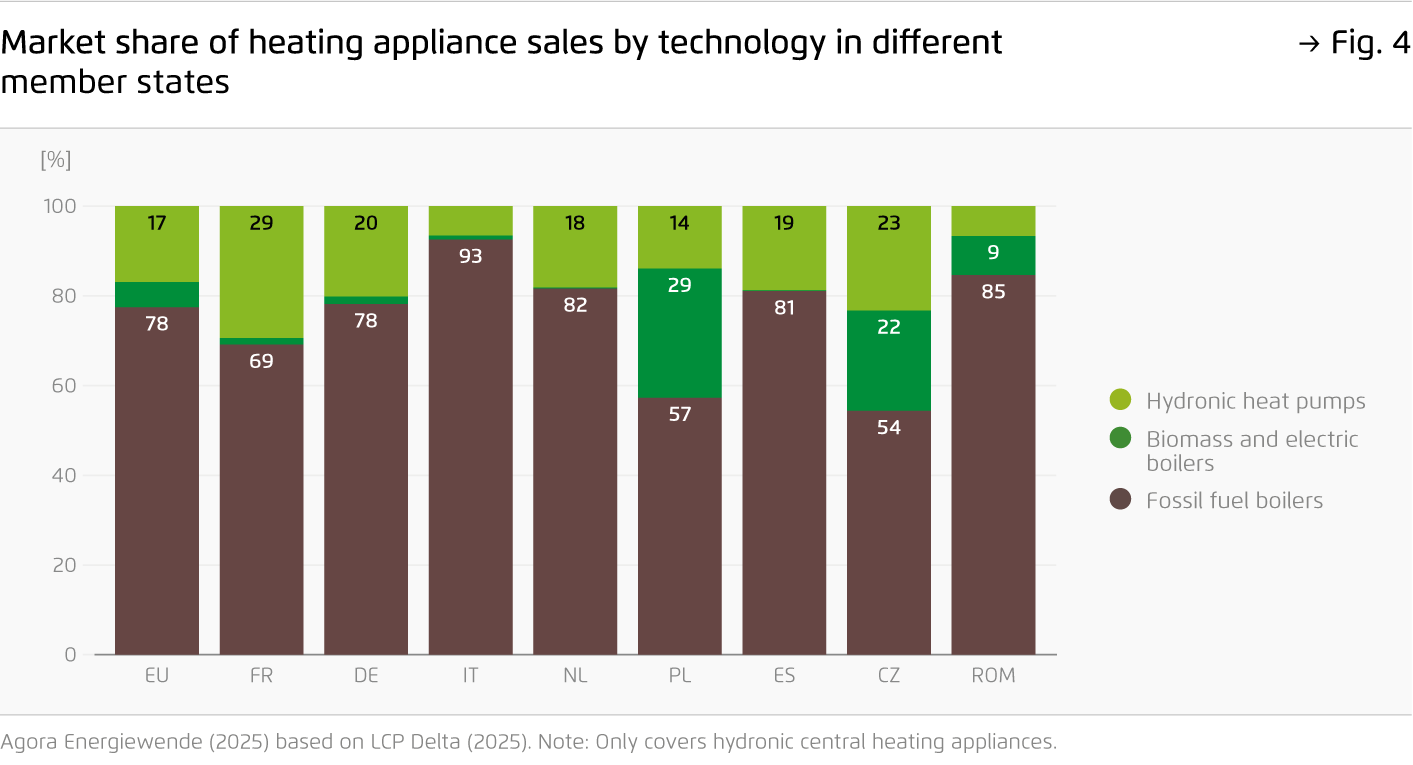
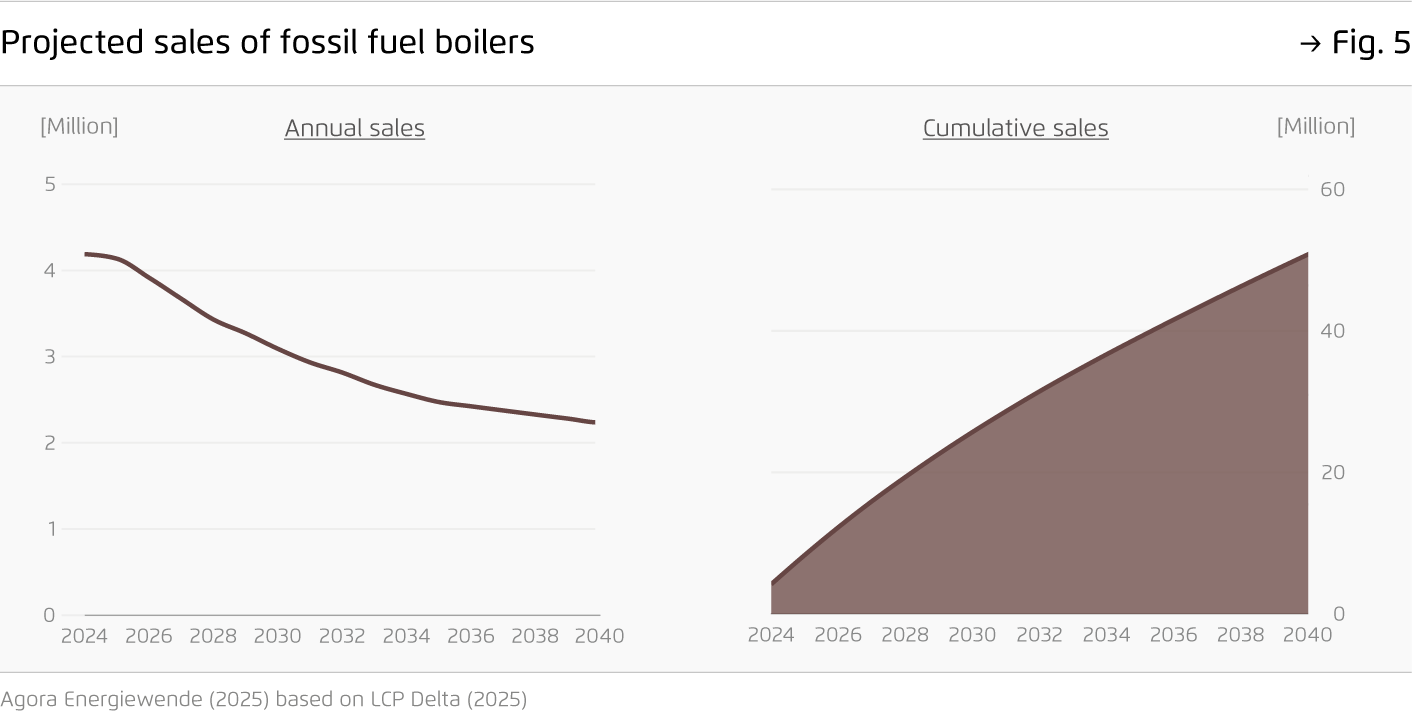
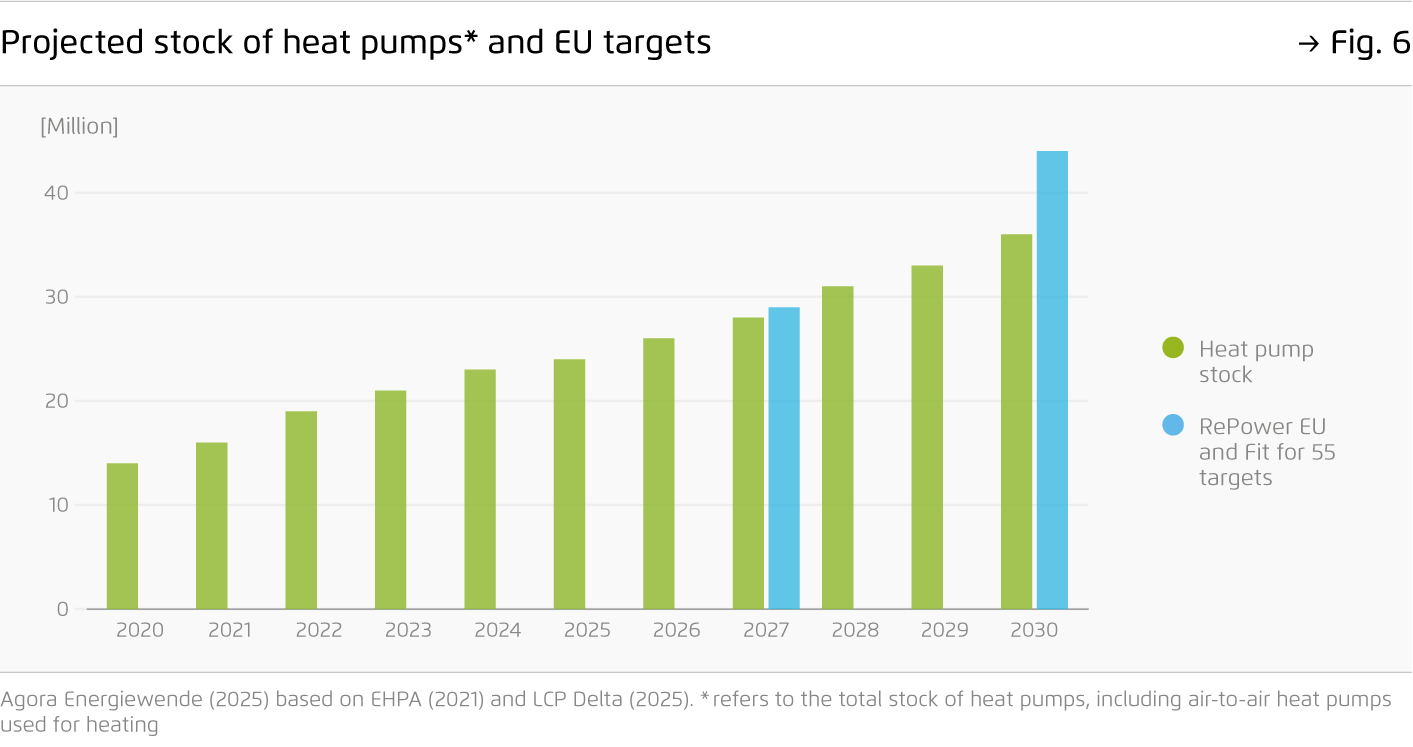
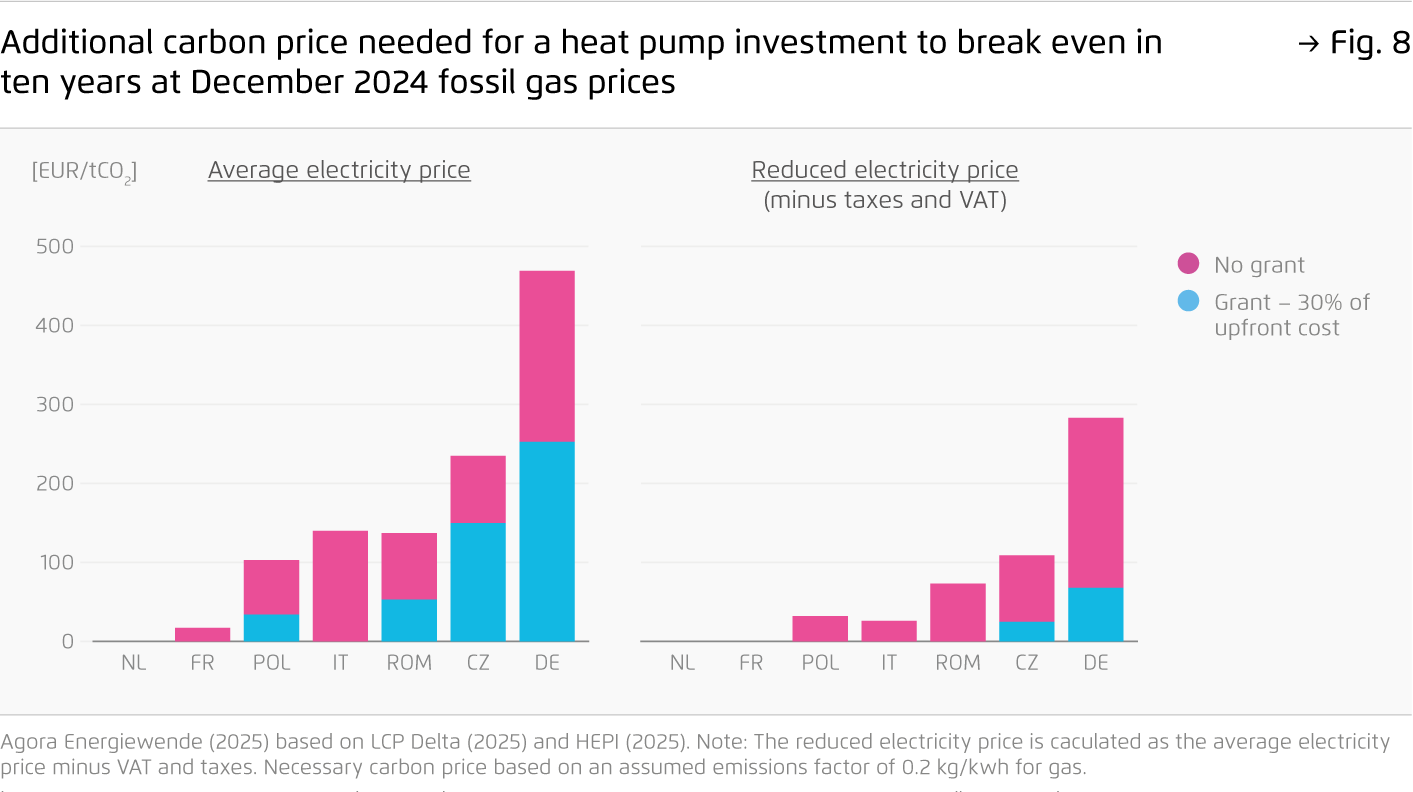
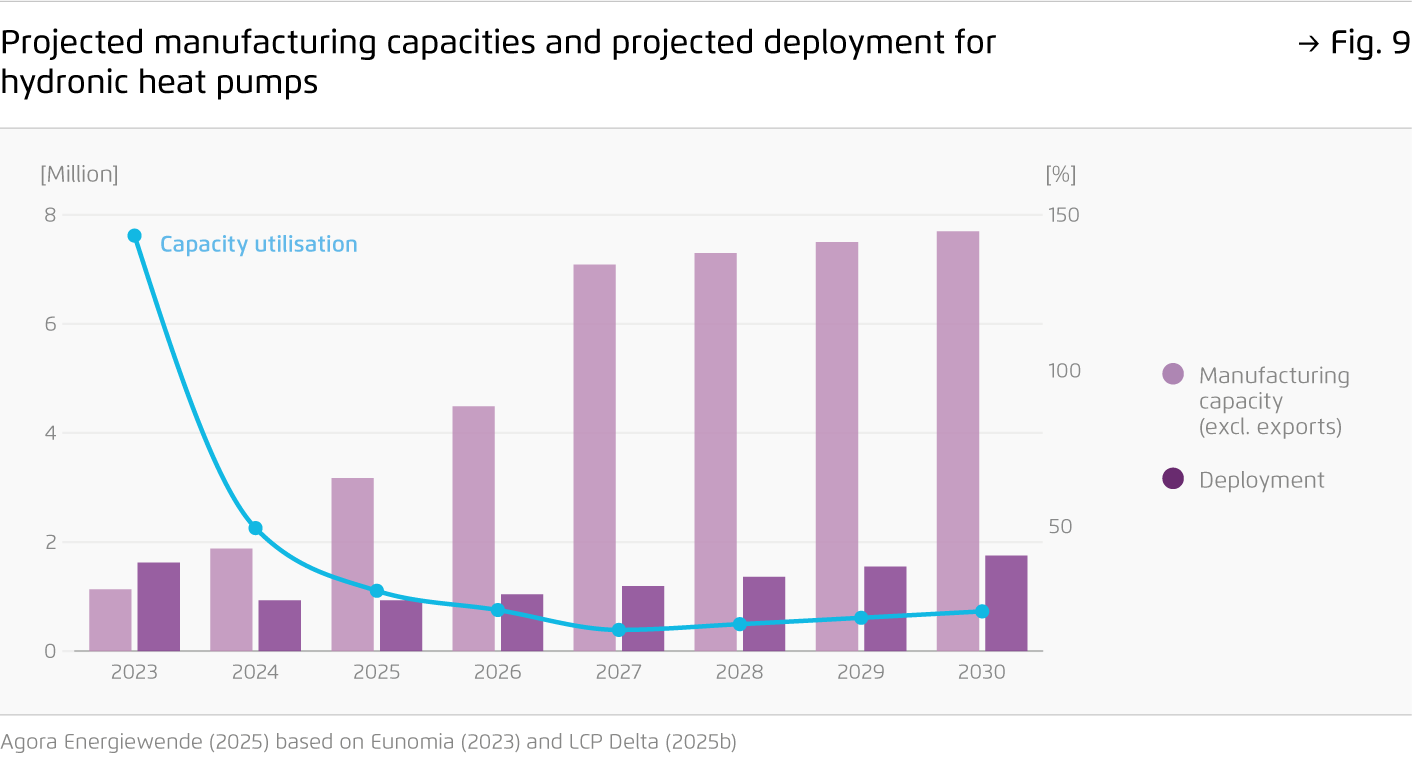
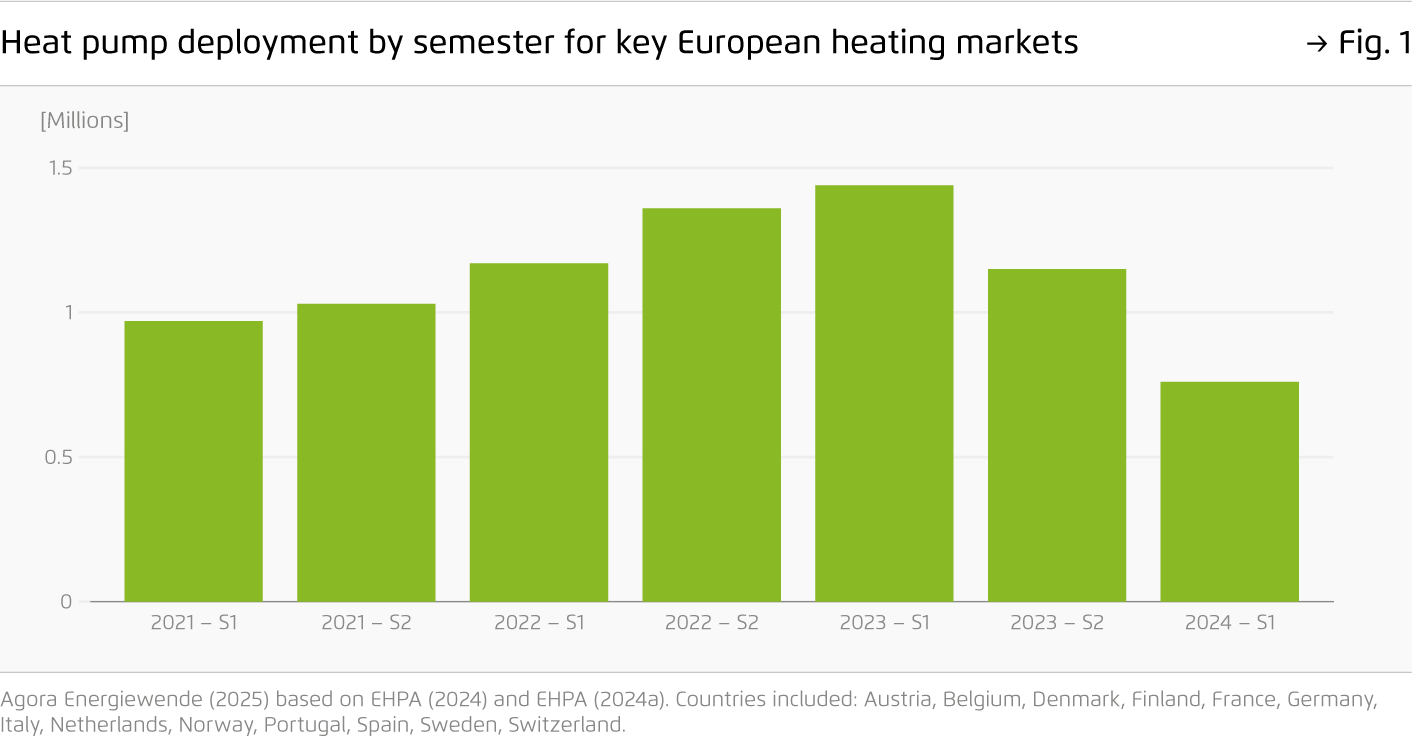
After soaring heat pump deployment during the energy crisis, sales of clean heating appliances have returned to 2021 levels. Without a strong policy signal, fossil gas boilers are set to dominate well into the 2030s, with more than 50 million boilers estimated to be installed cumulatively by 2040. Innovative approaches are needed to enhance energy security and preserve Europe’s competitive edge in cleantech.
-
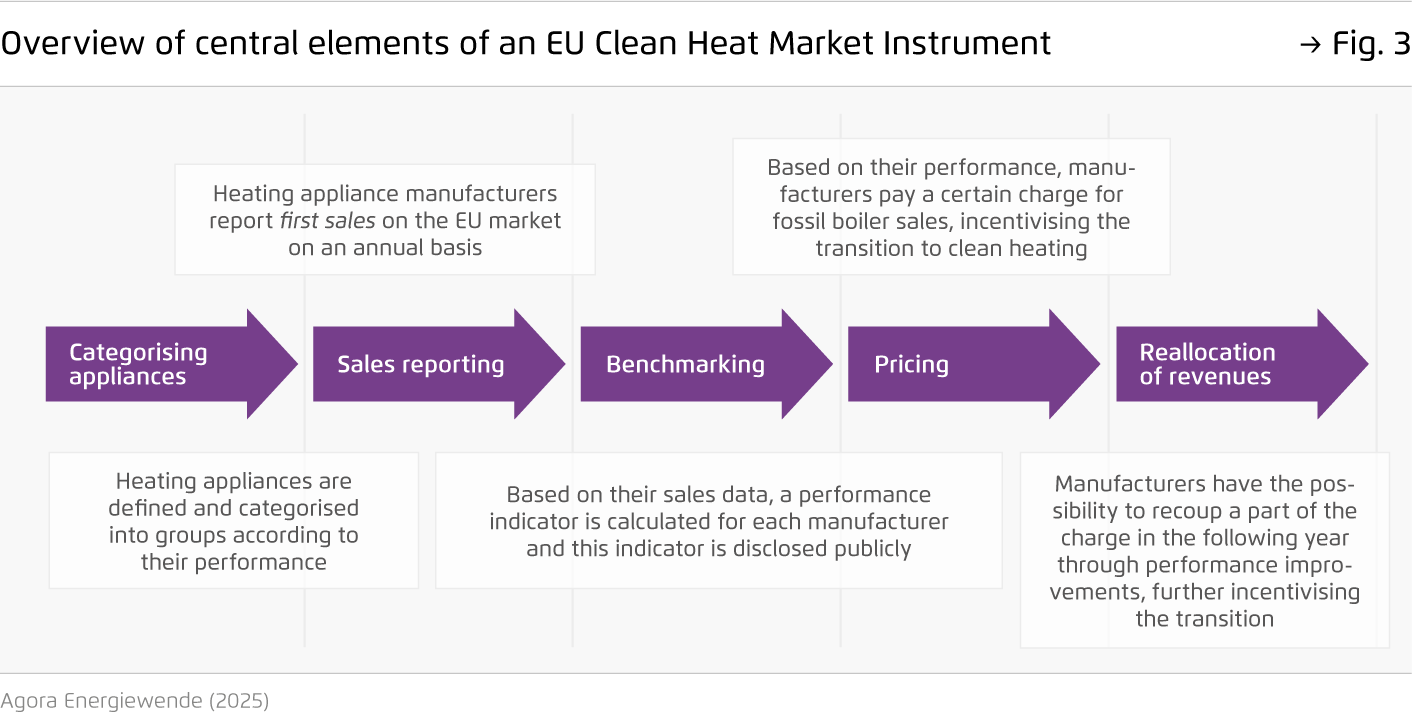
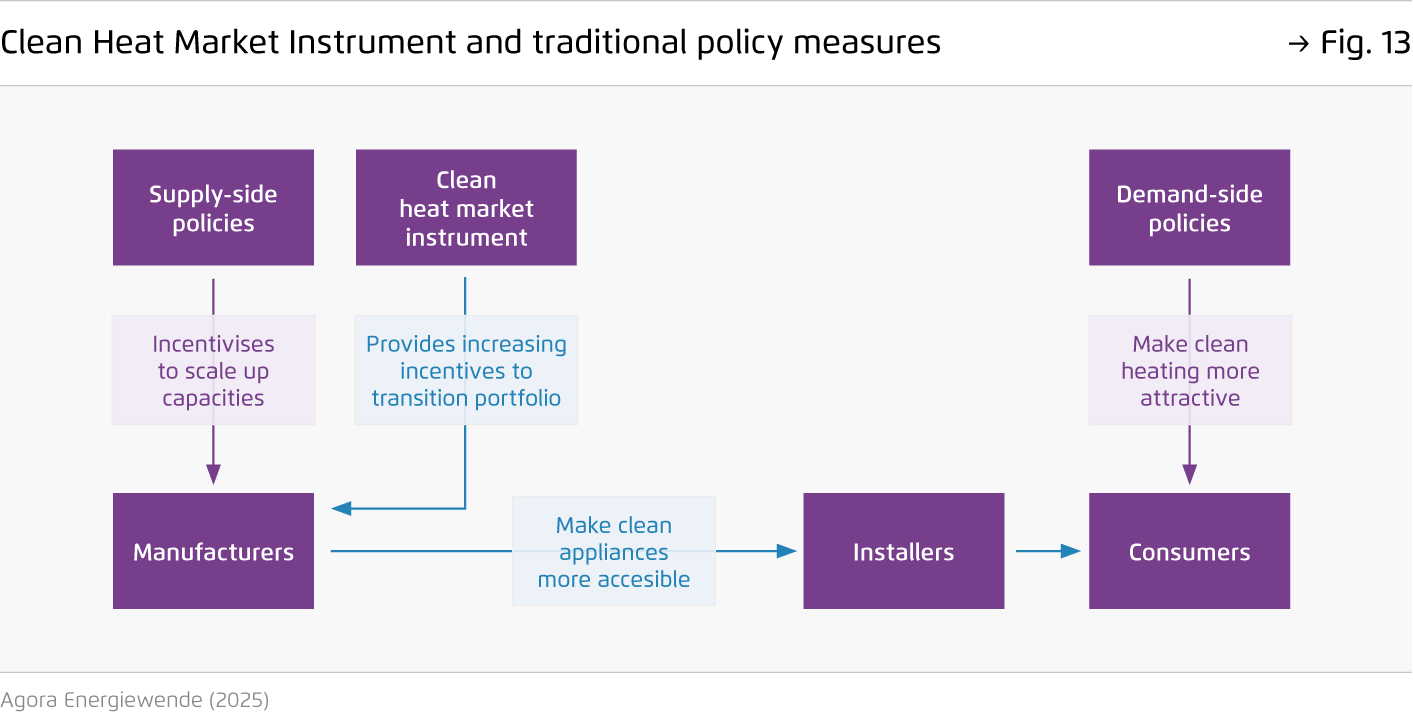
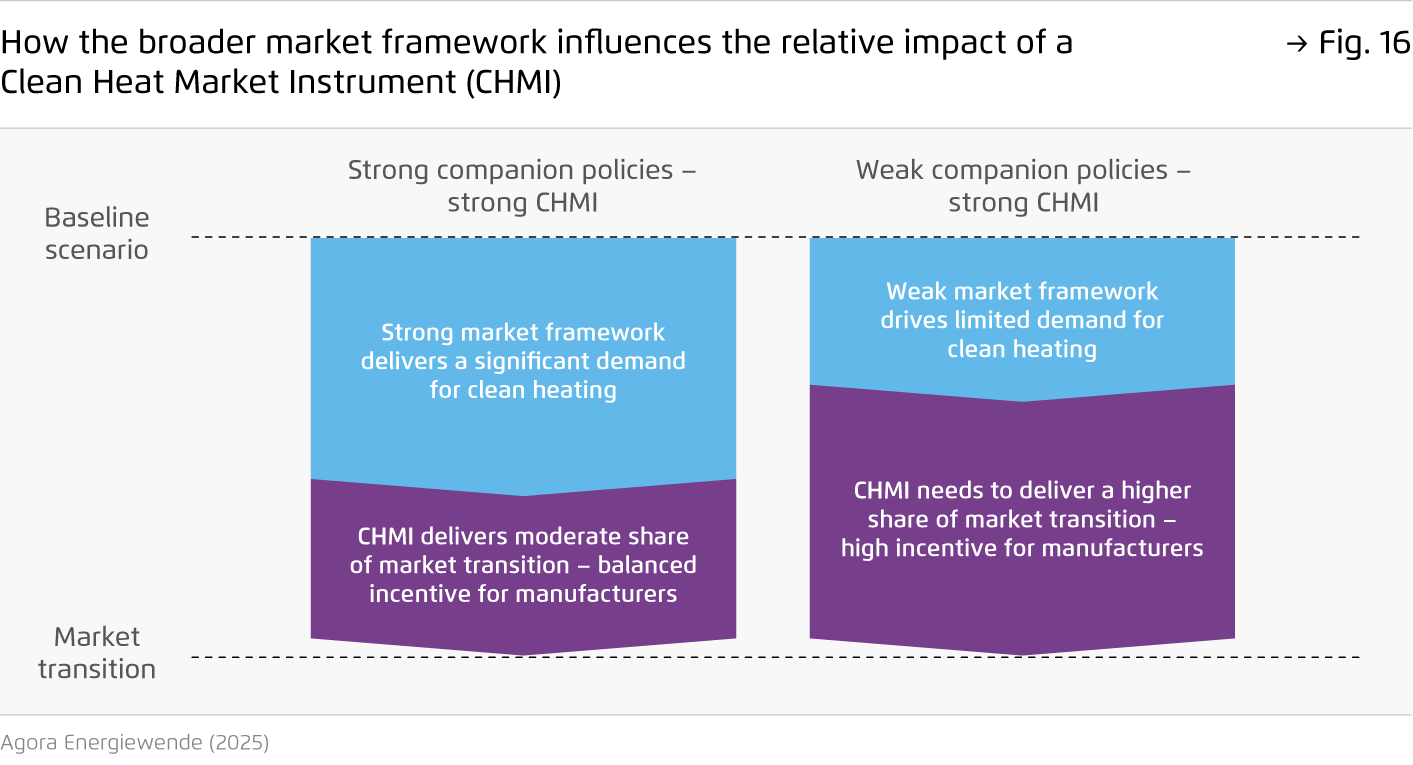
Based on incentives for manufacturers, an ‘EU Clean Heat Market Instrument’ could gradually expand the market for clean appliances.
One possible design would involve placing a charge on manufacturers based on the proportion of fossil fuel boilers in their sales. The revenue generated would then be reinvested into manufacturers who show progress in increasing their share of clean heating products. The charge level would be set by policymakers and could be gradually increased to maximise impact.
-
Strengthening the existing policy mix, the instrument would help chart a clear transition pathway for the European heating industry.
The instrument would complement policies such as the upcoming carbon pricing scheme for buildings and transport (‘ETS 2’). It would help meet the demand for clean heating appliances created by the ETS 2 by making those appliances more accessible and contribute to keeping the carbon price in check by reducing the installation of fossil fuel boilers.
-
The upcoming Clean Industrial Deal and planned Electrification Action Plan are an opportunity to start a strategic dialogue on the future of the European heating industry.
These initiatives aim to boost the competitiveness of European cleantech manufacturing and support the integration of the growing energy system. With buildings accounting for 40 percent of the EU’s energy consumption, accelerating the heating transition is crucial for meeting Europe’s energy and climate targets, enhancing competitiveness, and strengthening strategic autonomy.
Boosting the clean heat market
A policy for guiding the transition of the EU heating industry

Preface
The heating transition is vital to Europe’s energy transformation, offering benefits beyond emissions reduction – strengthening the European heating industry, enhancing energy security, and lowering household energy bills.
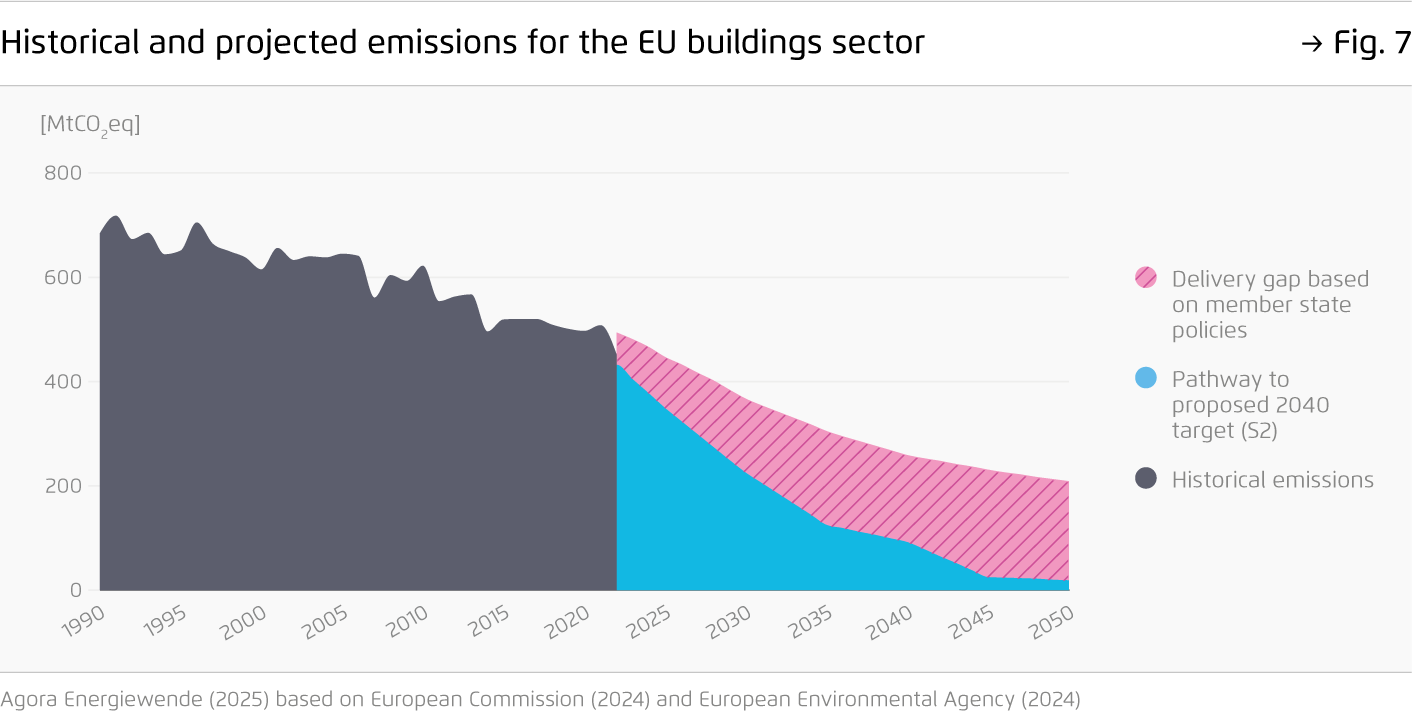
However, Europe’s heating transition is off track. With heating systems lasting 15–20 years, the continued market dominance of fossil fuel boilers is locking Europe into fossil fuel dependency, making the buildings sector a major challenge to achieving EU energy and climate targets for 2030 and 2040.
To accelerate the transition, a new industrial strategy is essential. The current policy framework fails to scale clean heating supply and demand, risking Europe’s leadership in this critical sector and the long-term competitiveness of its heating industry.
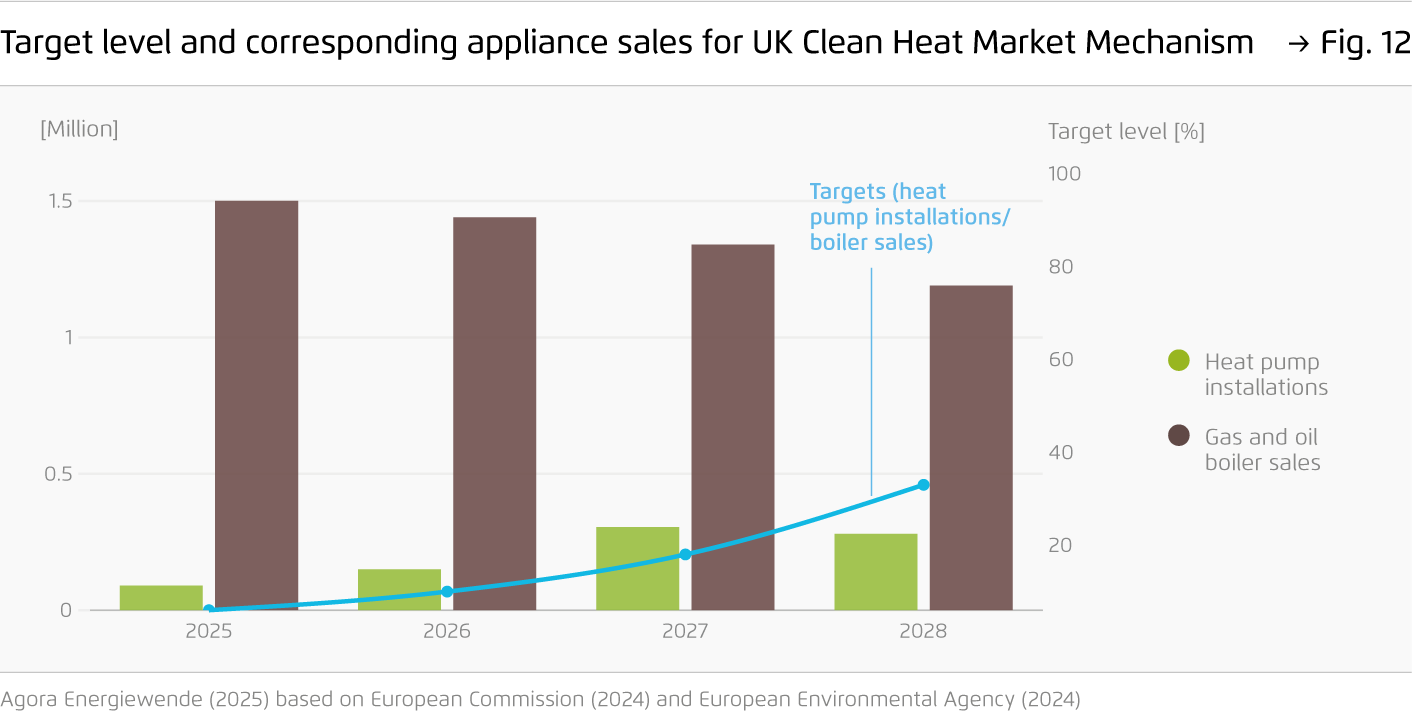
Inspired by the UK’s Clean Heat Market Mechanism and work done by the Regulatory Assistance Project on Clean Heat Standards, Agora Energiewende has explored the feasibility of an EU market-based instrument for heating appliances. Our findings suggest that an EU Clean Heat Market Instrument would enhance the effectiveness of other planned policies and could therefore help drive this transition post-2030.
But timely action is crucial. Political discussions must start now to enable legislation in this EU policy cycle. Let the debate begin!
Key findings
Bibliographical data
Downloads
-
Impulse
pdf 2 MB
Boosting the clean heat market
A policy for guiding the transition of the EU heating industry
All figures in this publication
Heat pump deployment by semester for key European heating markets
Figure 1 from Boosting the clean heat market on page 5
Projection of EU heating appliance sales by technology until 2040
Figure 2 from Boosting the clean heat market on page 6